A QR code is a special type of barcode that helps people quickly access digital information. If you’ve ever scanned a square code with your phone to open a website, menu, or payment page, you’ve used a QR code. The term QR code meaning comes from Quick Response, which shows how fast it works.
Unlike old barcodes, QR codes can store much more data. They can hold website links, text, contact details, Wi-Fi passwords, and even payment information. Today, QR codes are used everywhere, from restaurants and stores to banks, hospitals, schools, and travel tickets.
This guide explains what a QR code means, how QR codes work, the different types, real-life uses, safety tips, and future trends.
By the end, you’ll clearly understand why QR codes matter and how to use them safely and correctly.
QR Code Meaning in Simple Words
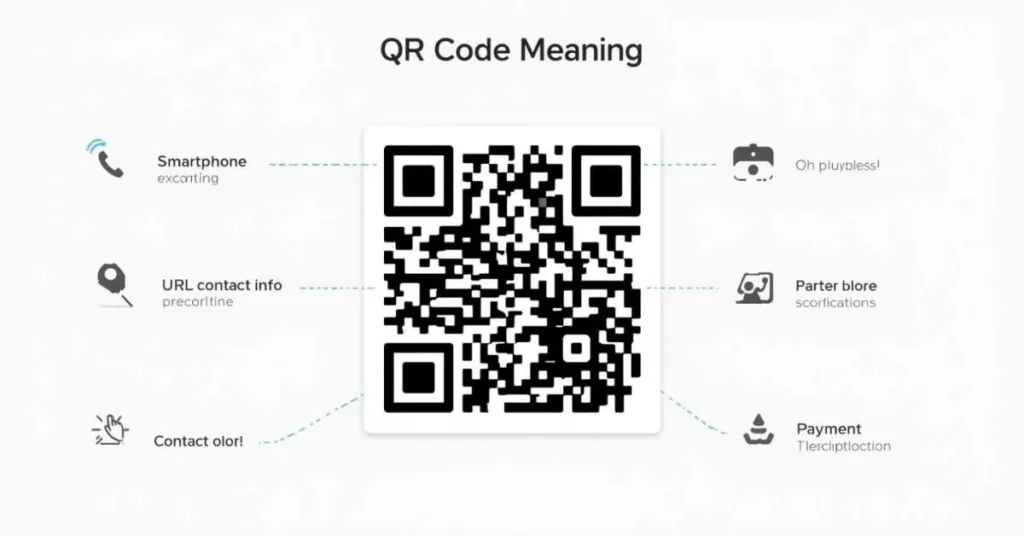
In simple terms, a QR code is a two-dimensional barcode that stores information in a square pattern. When scanned using a smartphone camera or QR scanner, it instantly shows the stored data.
QR code meaning:
👉 A fast way to share digital information using a scannable square code.
QR codes work faster than traditional barcodes and can be scanned from any angle. This makes them ideal for modern, contactless technology.
The History and Origin of QR Codes
QR codes were created in 1994 by Masahiro Hara, an engineer at Denso Wave, a company linked to Toyota. The original goal was to track car parts more efficiently during manufacturing.
The name Quick Response was chosen because the code could be read much faster than standard barcodes. Over time, QR codes moved beyond factories and into everyday life.
With the rise of smartphones, QR codes became widely used for marketing, payments, tickets, and information sharing. Today, QR codes connect the physical world to the digital world.
Interesting fact:
A QR code can store thousands of characters, while a normal barcode stores only a few dozen.
How QR Codes Work
A QR code is made of small black and white squares called modules. These modules represent encoded data. When a camera scans the code, the device decodes the pattern and displays the information.
QR codes can store:
- Website URLs
- Plain text
- Contact details (vCard)
- Wi-Fi login information
- Payment data
- Location details
How to Scan a QR Code (Step-by-Step)
- Open your phone’s camera or QR scanner app
- Point it at the QR code
- Wait for the scan prompt
- Tap to open the content
QR codes include error correction, so they still work even if part of the code is damaged or dirty.

Types of QR Codes
Static QR Codes
- Fixed information
- Cannot be edited after creation
- Best for permanent content like printed URLs
Dynamic QR Codes
- Editable after printing
- Allow scan tracking and analytics
- Ideal for marketing and business use
Specialized QR Codes
- Wi-Fi QR codes: Connect without typing passwords
- vCard QR codes: Save contact details instantly
- Payment QR codes: Used for digital wallets
- Event QR codes: Tickets for flights, concerts, or movies
Choosing the right type improves usability and results.
Common Uses of QR Codes in Daily Life
QR codes are popular because they are simple, fast, and cost-effective.
Marketing and Advertising
Businesses use QR codes on posters, packaging, and ads to send users to websites, apps, or social media.
Digital Payments
Banks and mobile wallets use QR codes for secure, contactless payments.
Restaurants and Hotels
QR codes provide digital menus, table ordering, and check-ins.
Events and Travel
Airlines, concerts, and cinemas use QR codes for tickets and verification.
Healthcare and Authentication
Many QR codes store medical records, vaccination certificates, and login verification.
QR Codes vs Barcodes: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
QR codes and barcodes are both used to store information, but they work in different ways. A barcode is one-dimensional (1D) and stores data in horizontal lines. It usually holds a small amount of information, such as a product number, and must be scanned from a specific angle.
A QR code is two-dimensional (2D) and stores data in a square pattern. It can hold much more information, including website links, text, contact details, and payment data. QR codes scan faster and work from any direction using a smartphone camera.
Barcodes are still common in retail and inventory systems, but QR codes are better for modern uses. They support contactless access, digital payments, tickets, and online content. Because QR codes are more flexible, faster, and easier to use, many industries now prefer them over traditional barcodes.
Why QR Codes Matter Today
QR codes are important because they:
- Save time
- Reduce physical contact
- Lower printing costs
- Improve user experience
- Work across devices
They support the shift toward contactless technology, making daily tasks faster and safer.
Advantages and Limitations of QR Codes
Advantages
- Fast and easy to scan
- Store many types of data
- Free or low-cost to create
- Work even when partly damaged
- Support analytics with dynamic codes

Limitations
- Can be misused for scams
- Damaged codes may fail
- Older phones may need scanner apps
- Users must scan safely
QR Code Security and Safety Tips
QR codes are safe when used correctly, but users should stay cautious.
Safe Scanning Tips
- Scan only trusted QR codes
- Avoid random codes on walls or emails
- Check the URL before opening
- Use security-enabled QR scanner apps
- Watch for stickers placed over real codes
Dynamic QR codes also allow creators to disable unsafe links.
Fun Facts and the Future of QR Codes
- QR codes were first made for cars
- Their use exploded during the pandemic
- Future QR codes may trigger AR experiences
- Blockchain may use QR codes for secure verification
- Smart cities and IoT devices rely on QR scanning
QR codes will continue to evolve as digital access grows.
Frequently Asked Questions About QR Codes
What is the difference between a QR code and a barcode?
Barcodes are one-dimensional and store less data. QR codes are two-dimensional and store much more information.
Can QR codes expire?
Static QR codes do not expire. Dynamic QR codes can be disabled.
Are QR codes safe?
Yes, when scanned from trusted sources.
Do QR codes need the internet?
Only QR codes linking to online content need internet access.
Conclusion
The QR code meaning goes beyond a simple barcode. QR codes are powerful tools that connect physical items to digital information instantly. From payments and menus to tickets and authentication, they simplify modern life.
Knowing how QR codes work, the different types, how to use them, and how to stay safe helps people and businesses use them easily. As technology advances, QR codes will remain a key part of the digital world.
Click Here To Read About: What Does It Mean If Your White Blood Cell Count Is High?

Hi, I’m Geoffrey Chaucer. I explore the stories and meanings behind words, turning ideas into clear, insightful writing. Through every article I craft, I aim to spark curiosity, share knowledge, and help readers uncover practical, meaningful truths in everyday life.