Have you ever glanced at your phone and noticed LTE and wondered, “What does LTE mean on my phone?” Well, LTE, or Long Term Evolution, is the technology behind most 4G connections today. In other words, it provides high-speed mobile internet without relying on WiFi. As a result, you can browse websites quickly, stream in HD, download apps, and even make HD calls using VoLTE.
Furthermore, devices from Apple, Samsung, and Qualcomm-powered phones automatically connect to LTE networks. Even if your device supports 5G, LTE often appears when coverage is weak, acting as a stable fallback. Therefore, understanding LTE is important for daily mobile use. In this guide, we will explain everything about LTE, LTE+, VoLTE, 4G, 3G, and 5G. Moreover, you will learn how to check LTE on your device and troubleshoot common LTE issues effectively.
What LTE Stands For
LTE stands for Long Term Evolution, and it was developed by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). Essentially, LTE enhances speed, reliability, and efficiency compared to 3G.
For example, devices like Apple iPhones, Samsung Galaxy phones, and Qualcomm-powered Androids use LTE to:
- Browse websites quickly
- Stream HD videos smoothly
- Download apps and files rapidly
- Make HD calls using VoLTE
Additionally, LTE powers LTE+ (LTE Advanced), which combines multiple frequency bands to deliver higher speeds and improved coverage. Even with 5G availability, LTE remains essential for stable connectivity, especially in indoor or rural areas.
LTE vs 4G vs 3G vs 5G
To better understand LTE, it helps to compare it with other networks.
| Network | Generation | Speed (Typical) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3G | Third | 0.5–3 Mbps | Basic browsing and calls |
| LTE (4G) | Fourth | 10–100 Mbps | Smooth streaming, apps, HD VoLTE |
| LTE+ | Enhanced 4G | 100–300 Mbps | Carrier aggregation, better coverage |
| 5G | Fifth | 100–1000+ Mbps | Ultra-HD streaming, gaming, IoT |
In short, LTE is the technology powering 4G networks, which explains why carriers often display 4G LTE. Consequently, LTE provides higher speeds than 3G, but it is slower than 5G.
Is LTE Fast?
Yes, LTE provides high-speed mobile internet. For instance:

Typical LTE speeds:
- Download: 10–100 Mbps
- Upload: 5–50 Mbps
However, several factors affect speed:
- Signal strength – stronger signals result in faster speeds
- Network congestion – crowded areas may slow connections
- Device performance – newer phones handle LTE better
- Distance from cell towers – closer proximity improves speed
Therefore, with LTE+, speeds can increase significantly, enabling smooth HD streaming, gaming, and large downloads.
What Is LTE+ (LTE Advanced)?
LTE+ is an upgraded LTE technology that uses carrier aggregation to combine multiple frequency bands. As a result, it delivers faster speeds and better coverage.
| Feature | LTE | LTE+ |
|---|---|---|
| Avg Download Speed | 10–100 Mbps | 100–300 Mbps |
| Avg Upload Speed | 5–50 Mbps | 20–100 Mbps |
| Latency | Moderate | Low |
| Coverage | Wide | Enhanced in crowded areas |
Thus, LTE+ ensures superior performance, especially where 5G is unavailable.
What Is VoLTE?
VoLTE (Voice over LTE) allows voice calls over LTE instead of 3G networks.
Benefits include:
- HD voice quality
- Ability to use apps while calling
- Faster call setup
- Better battery efficiency
In fact, most modern phones, including iPhones and Samsung Galaxy devices, automatically enable VoLTE on carriers like T-Mobile and Verizon.
How LTE Works
LTE connects your phone to nearby cell towers using radio waves. Subsequently, data travels in packets through the carrier network to the internet.
Key techniques include:
- MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output): multiple antennas increase speed and reliability
- Carrier Aggregation: combines frequency bands for faster internet
- Low Latency Routing: reduces delays for apps and games
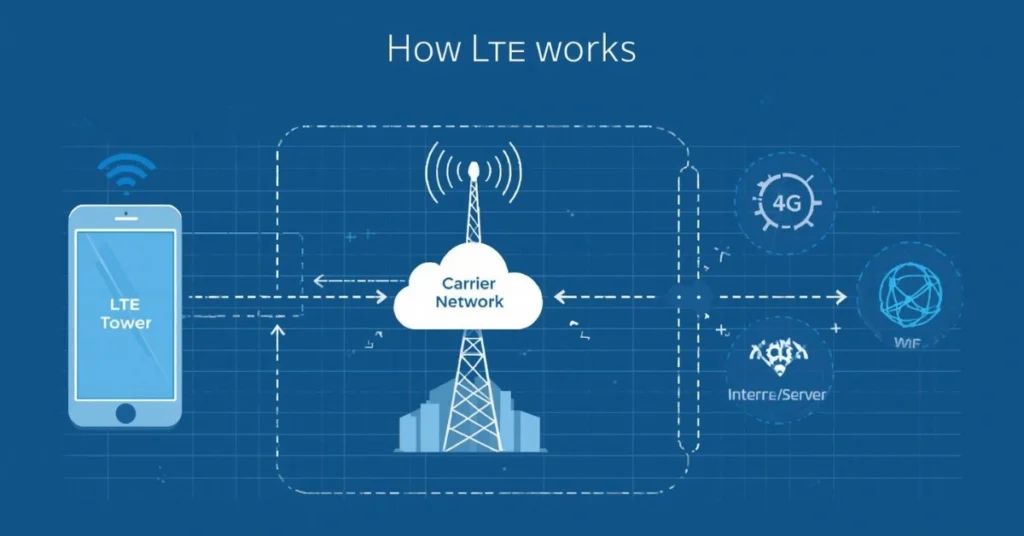
Therefore, LTE ensures a stable and fast mobile experience.
Why Is My LTE Slow?
Common reasons for slow LTE include:
- Weak signal indoors or in rural areas
- Network congestion in crowded locations
- Carrier throttling after data limits
- Device software issues
Solutions include:
- Toggle airplane mode
- Restart your phone
- Reset network settings
- Move near a window or outdoors
- Update carrier settings
Hence, troubleshooting LTE issues often restores optimal performance.
Does LTE Work Without WiFi?
Yes. LTE functions independently of WiFi, providing internet wherever cellular coverage exists. Phones automatically switch between WiFi and LTE to maintain the best connection.
Does LTE Cost Extra?
Most modern plans include LTE. However, limited plans may incur extra charges if the data cap is exceeded. Therefore, using WiFi whenever possible helps save mobile data.
How to Check LTE Support on Your Phone
- Check phone specs online
- Navigate to Settings → Mobile Network → Network Mode
- Use IMEI checks on carrier websites
- Refer to carrier support lists for LTE and LTE+
As a result, you can verify LTE compatibility before purchase or troubleshooting.
Is LTE Safe?
Yes. LTE uses non-ionizing radio waves, which are safe. Phones adhere to strict regulatory standards. Additionally, using speakerphone or hands-free reduces exposure further.
How to Check LTE Signal Strength on Your Phone
- iPhone: Settings → Cellular → Field Test Mode
- Android / Samsung: Dial
*#*#4636#*#*→ Phone Info → Signal Strength
| Signal (dBm) | Quality | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| -50 to -70 | Excellent | Strong connection |
| -70 to -90 | Good | Reliable |
| -90 to -110 | Poor | Slow/unstable |
| < -110 | Very Weak | Likely no connection |
Thus, checking signal strength helps diagnose connectivity issues effectively.
Carrier-Specific LTE Notes (T-Mobile, Verizon, AT&T, Sprint)
| Carrier | LTE Coverage | LTE+ | VoLTE | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-Mobile | Nationwide | Yes | Yes | LTE fallback when 5G unavailable |
| Verizon | Nationwide | Yes | Yes | Strong indoor coverage |
| AT&T | Nationwide | Yes | Yes | Combines LTE+ & VoLTE for HD calls |
| Sprint | Limited (Merged with T-Mobile) | Yes | Yes | LTE still widely used post-merger |
Therefore, understanding your carrier’s LTE network can explain speed variations.
Device-Specific LTE Notes (iPhone vs Samsung)
Apple iPhones:
- LTE auto-enabled
- VoLTE enabled by default
- LTE+ improves speed in crowded areas
Samsung Galaxy Phones:
- LTE/LTE+ displayed depending on carrier
- Signal bars indicate strength
- Manual LTE selection in Settings → Mobile Network → Network Mode
In short, device behavior can affect LTE performance and visibility.
Future of LTE: Sunset or Coexistence with 5G
Although 5G is rolling out, LTE remains essential:
- Coverage: LTE reaches areas where 5G is unavailable
- Reliability: LTE has proven stable for years
- Device compatibility: LTE, LTE+, and 5G coexist on many phones
- Expected timeline: LTE is projected to remain active for at least another decade
| Feature | LTE | 5G |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 10–300 Mbps | 100–1000+ Mbps |
| Latency | Moderate | Ultra-low |
| Coverage | Wide | Limited initially |
| Device Compatibility | Most phones | Newer models only |
Hence, LTE will continue as a fallback even with 5G expansion.
Troubleshooting Common LTE Issues
Common problems:
- Slow download/upload
- LTE icon not appearing
- Calls dropping
- LTE switches to 3G
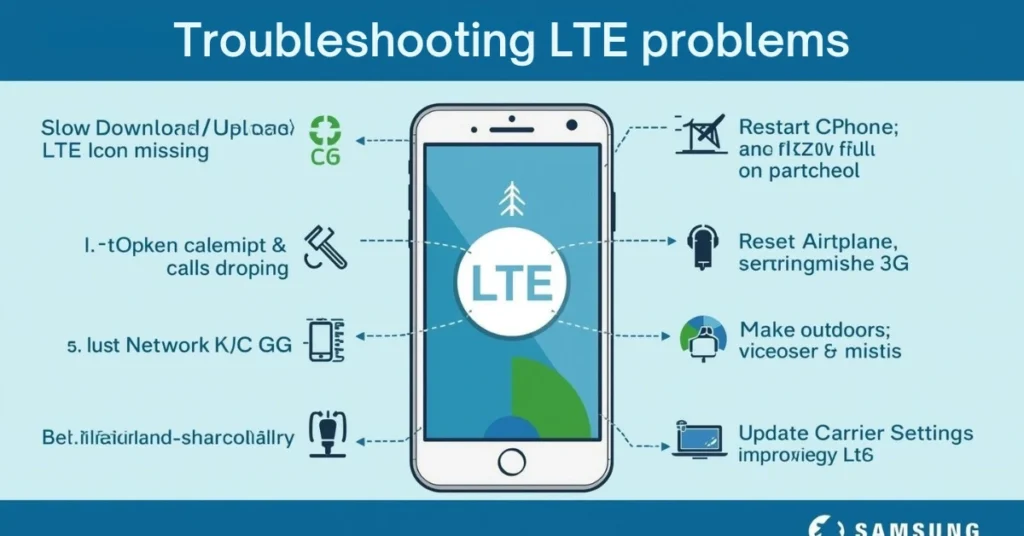
Solutions:
- Restart your phone
- Toggle airplane mode
- Reset network settings
- Move to an open area
- Update carrier settings
Consequently, these steps often restore LTE performance.
Advanced LTE Technologies You Should Know
Beyond basic LTE, advanced technologies improve speed, reliability, and efficiency:
- MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output): uses multiple antennas to boost speed and coverage
- Carrier Aggregation: combines multiple frequency bands for higher data rates
- LTE Broadcast: allows multiple users to stream the same content efficiently
- Low Latency LTE: reduces delay for gaming, video calls, and real-time apps
Thus, understanding LTE technology explains why Samsung Galaxy and iPhones perform better in certain areas.
Tips to Optimize Your LTE Connection
Even with LTE, there are ways to maximize speed:
| Tip | How it Helps |
|---|---|
| Keep phone software updated | Optimizes LTE performance |
| Enable LTE+ | Boosts speed via carrier aggregation |
| Use WiFi where possible | Reduces strain on LTE and saves data |
| Avoid peak hours | Network congestion slows speeds |
| Position near windows | Better indoor reception |
| Reset network settings occasionally | Clears misconfigured LTE settings |
For example, enabling LTE+ on a Samsung phone in a crowded urban area can increase download speed from 50 Mbps to 200 Mbps.
Real-World Uses of LTE
LTE impacts daily life in many ways:
- Streaming HD Video: watch YouTube, Netflix, and other platforms without buffering
- Gaming on Mobile: low latency improves real-time games
- Mobile Office: access emails, video conferences, and cloud apps
- VoLTE Calls: make high-quality voice calls while using apps
- Emergency Connectivity: ensures reliable access when WiFi fails
Therefore, LTE remains essential even as 5G rolls out.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is LTE the same as 4G? – LTE is the technology; 4G is the generation label. Practically the same.
- Why does LTE disappear sometimes? – Weak signal or fallback to 3G/5G.
- Can I make calls on LTE? – Yes, via VoLTE.
- Why does LTE switch to 3G? – LTE coverage is weak.
- Will LTE be replaced by 5G? – LTE will coexist with 5G for many years.
- How to fix slow LTE? – Restart, toggle airplane mode, reset network settings.
Quick Summary
LTE (Long Term Evolution) is the backbone of 4G networks worldwide. Devices from Apple, Samsung, and Qualcomm rely on LTE for fast internet, HD calls, and reliable connectivity. LTE+ and VoLTE further enhance speed and call quality. While 5G is the future, LTE remains crucial for stability, coverage, and device compatibility.
Click Here to Read More About : what does compromise mean

Hi, I’m Geoffrey Chaucer. I explore the stories and meanings behind words, turning ideas into clear, insightful writing. Through every article I craft, I aim to spark curiosity, share knowledge, and help readers uncover practical, meaningful truths in everyday life.